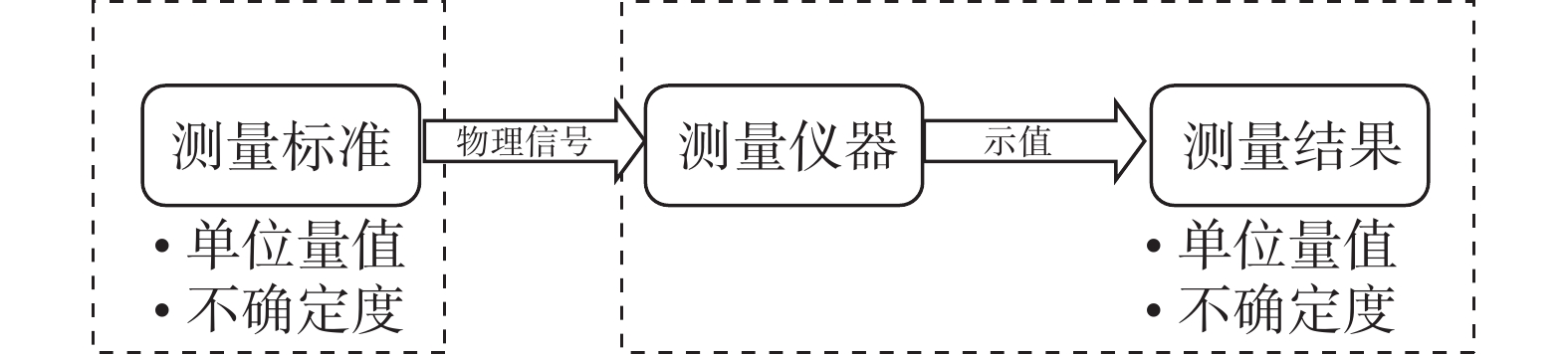
| [1] |
Rojko A. Industry 4.0 concept: Background and overview[J]. International Journal of Interactive Mobile Technologies, 2017, 11(5): 77-90. doi: 10.3991/ijim.v11i5.7072
|
| [2] |
Dalenogare L S, Benitez G B, Ayala N F, et al. The expected contribution of Industry 4.0 technologies for industrial performance[J]. International Journal of Production Economics, 2018, 204: 383-394. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpe.2018.08.019
|
| [3] |
Ghobakhloo M. Industry 4.0, digitization, and opportunities for sustainability[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 252: 119869. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119869
|
| [4] |
Wang J, Wu H, Chen Y. Made in China 2025 and manufacturing strategy decisions with reverse QFD[J]. International Journal of Production Economics, 2020, 224: 107539. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpe.2019.107539
|
| [5] |
Zhong R Y, Xu X, Klotz E, et al. Intelligent manufacturing in the context of industry 4.0: a review[J]. Engineering, 2017, 3(5): 616-630. doi: 10.1016/J.ENG.2017.05.015
|
| [6] |
Chen Y. Integrated and intelligent manufacturing: perspectives and enablers[J]. Engineering, 2017, 3(5): 588-595. doi: 10.1016/J.ENG.2017.04.009
|
| [7] |
Durakbasa N M, Bas G, Bauer J M, et al. Development of an advanced metrology and intelligent quality management as a strategic approach in manufacturing industry[C]. LMPMI, 2014.
|
| [8] |
Yin P, Wang J, Lu C. Measuring software test verification for complex workpieces based on virtual gear measuring instrument[J]. Measurement Science Review, 2017, 17(4): 197-207. doi: 10.1515/msr-2017-0023
|
| [9] |
汤洁, Härtig F, 石照耀. 计量软件溯源中的TraCIM软件认证系统[J]. 工具技术, 2017, 51(12): 4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7008.2017.12.031
|
| [10] |
Hopp T H, Levenson M S. Performance Measures for Geometric Fitting in the NIST Algorithm Testing and Evaluation Program for Coordinate Measurement Systems[J]. Journal of Research of the National Institute of Standards and Technology, 1995, 100(5): 563-574. doi: 10.6028/jres.100.042
|
| [11] |
Velychko O M, Gaman V V, Gordiyenko T B, et al. Testing of measurement instrument software with the purpose of conformity assessment[J]. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 2019, 97: 19-26.
|
| [12] |
Boccardo D R, Machado R C S, Camara S M, et al. Software validation of medical instruments[C]. IEEE, 2014.
|
| [13] |
崔伟群. 计量器具软件测评体系研究[J]. 中国计量, 2010, 174(5): 68-69. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9364.2010.05.032
|
| [14] |
李东升, 郭天太. 量值传递与溯源[M]. 杭州: 浙江大学出版社, 2009.
|
| [15] |
Matsumoto E. The History of Electric Measuring Instruments and Active Components[C]. IEEE, 2004.
|
| [16] |
Yang F Q. Thinking on the development of software engineering technology[J]. Journal of software, 2005, 16(1): 1-7. doi: 10.1360/jos160001e
|
| [17] |
崔伟群. 欧盟关于计量器具软件测评的现状与发展[J]. 中国计量, 2012(8): 19-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9364.2012.08.010
|
| [18] |
Roy B K, Santhosh K V. An intelligent instrument for measuring liquid level[C]. IEEE, 2011.
|
| [19] |
Topolsky D V, Topolskaya I G, Topolsky N D. Intelligent instrument transformer for control systems of digital substations[C]. IEEE, 2018.
|
| [20] |
Khanafer M, Shirmohammadi S. Applied AI in instrumentation and measurement: The deep learning revolution[J]. IEEE Instrumentation & Measurement Magazine, 2020, 23(6): 10-17.
|
| [21] |
Cai L, Gao J, Zhao D. A review of the application of deep learning in medical image classification and segmentation[J]. Annals of Translational Medicine, 2020, 8(11): 713. doi: 10.21037/atm.2020.02.44
|
| [22] |
Shu X, Wang X, Zang X, et al. Large-Scale Spatio-Temporal Person Re-identification: Algorithms and Benchmark[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2021, 32(7): 4390-4403.
|
| [23] |
Wu D, Zheng S J, Zhang X P, et al. Deep learning-based methods for person re-identification: A comprehensive review[J]. Neurocomputing, 2019, 337: 354-371. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2019.01.079
|
| [24] |
崔伟群, 田锋, 李颖. 数字计量学导论[M]. 北京: 中国质检出版社, 2014.
|
| [25] |
靳浩元, 刘军. 测量不确定度的评定方法及应用研究[J]. 计量科学与技术, 2021, 65(5): 124-131. doi: 10.12338/j.issn.2096-9015.2020.9002
|
| [26] |
汪斌, 卢晓华. 一元线性校准曲线不确定度评定与适用条件的讨论[J]. 计量科学与技术, 2022, 66(7): 45-49, 44.
|
| [27] |
Thiel F. Digital transformation of legal metrology-the European metrology cloud[J]. OIML Bulletin, 2018, 59(1): 10-21.
|
| [28] |
Chalk S J, Coppa D N, Flamenco F, et al. International development of the SI in FAIR digital data[J]. Measurement: Sensors, 2021, 18: 100293. doi: 10.1016/j.measen.2021.100293
|
| [29] |
Neyezhmakov P, Zub S, Pivnenko S. Preliminary E-infrastructure for Digital Calibration Certificate[J]. Measurement: Sensors, 2021, 18: 100332. doi: 10.1016/j.measen.2021.100332
|
| [30] |
窦晨, 周自力. 数字世界计量的重要性及计量的发展方向探析[J]. 计量科学与技术, 2022, 66(9): 70-73. doi: 10.12338/j.issn.2096-9015.2022.0168
|
| [31] |
Varshney A, Garg N, Nagla K S, et al. Challenges in sensors technology for industry 4.0 for futuristic metrological applications[J]. MAPAN, 2021, 36(2): 215-226. doi: 10.1007/s12647-021-00453-1
|


 作者投稿
作者投稿 专家审稿
专家审稿 编辑办公
编辑办公


 下载:
下载: