A Study on Quality Assessment of Human Genome Data
-
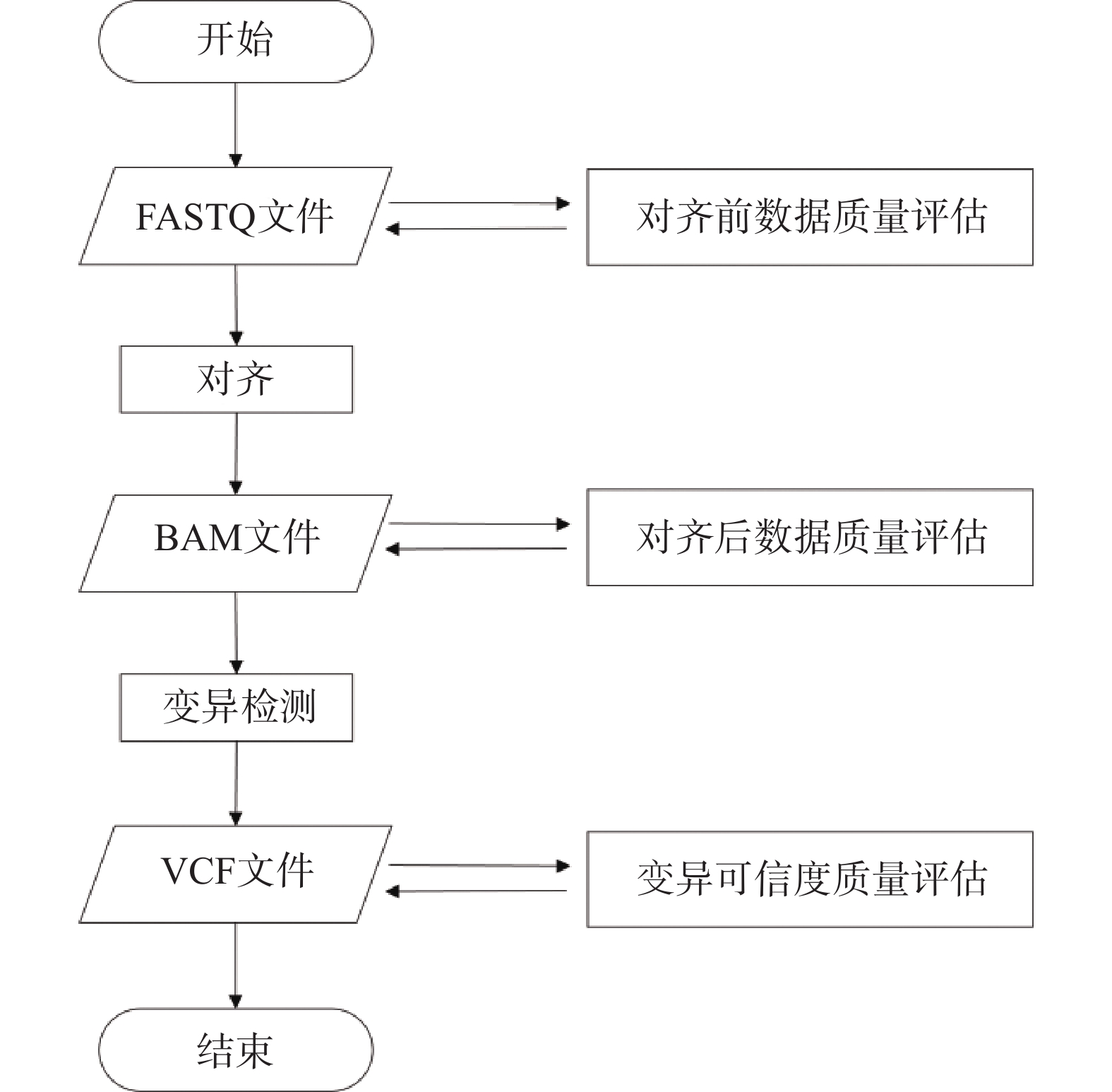
摘要: 随着高通量测序技术的发展,研究人员现已具备对人类基因组测序数据进行深度分析和处理的能力,数据质量无疑成为影响数据分析结果可信度的决定性因素。因此,精确的数据质量评估成为至关重要的环节,其目的在于避免不必要的损失并确保结果的准确性。学术界和产业界都高度重视数据质量的评估,提出了大量的质量评估方法并开发了大量的工具,例如FastQC、Qualimap等软件工具,以及各类标准物质和标准参考数据,为数据质量评估提供了有力支持。然而,系统的研究各个质量评估环节的工具集以及对各类工具集的特点汇总相对较少,数据的质量评估的过程仍存在诸多问题和挑战。为评估人类基因组数据工作提供帮助,深入分析了上述问题的解决策略,并提供了一些具有实践意义的建议,以期提供参考。Abstract: In the wake of the advancements in high-throughput sequencing technology, researchers are now equipped with the capacity to conduct in-depth analyses and processing of human genome sequencing data. The quality of these data inevitably serves as a pivotal factor impacting the credibility of analysis results. As such, precise quality assessment becomes a paramount process to circumvent needless loss and to ascertain the accuracy of outcomes. Both the academic and industrial communities place significant emphasis on data quality assessment, having introduced numerous methods for such assessment and developed a multitude of tools like FastQC and Qualimap software, along with various standard materials and standard reference data, which collectively underpin data quality assessment. However, there are scant systematic investigations of toolsets employed in each assessment stage and summarizations of toolset characteristics. Furthermore, the process of data quality assessment is laden with numerous issues and challenges. To aid human genome data assessment endeavors, this paper delves into potential solutions for these problems and puts forth several practically significant suggestions for reference.
-
Key words:
- metrology /
- human genome /
- data /
- quality assessment /
- assessment metrics /
- tools
-
表 1 各类对齐前质量评估工具的评估指标比较
Table 1. Comparison of evaluation metrics for various pre-alignment quality assessment tools
评估指标 FastQC fastp NGS QC Toolkit HTQC SolexaQA SOAPnuke BIGpre FastQ Screen 总读取数量 √ √ √ √ √ √ 读长分布 √ √ √ √ √ 碱基分布 √ √ √ √ √ GC含量 √ √ √ √ 质量分数 √ √ √ √ √ √ √ 接头序列的污染 √ √ 其他物种的污染 √ 序列重复水平 √ √ 过度表达的序列 √ k-mer分析 √ √ 表 2 各类对齐前质量评估工具的特点和下载链接
Table 2. Characteristics and download links for various pre-alignment quality assessment tools
工具 特点 下载链接 FastQC 评估指标较为全面 https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/ HTQC 评估、序列修剪 https://sourceforge.net/projects/htqc/ NGS QC Toolkit 评估、序列修剪 https://github.com/mjain-lab/NGSQCToolkit fastp 双端测序评估、修剪 https://github.com/OpenGene/fastp SolexaQA 序列根据质量分类 https://solexaqa.sourceforge.net/ BIGpre 检测、处理重复序列 http://bigpre.sourceforge.net/ FastQ Screen 污染评估 https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastq_screen/ SOAPnuke MapReduce加速 https://github.com/BGI-flexlab/SOAPnuke RabbitQC 充分利用硬件加速 https://github.com/ZekunYin/RabbitQC 表 3 流行的短读取对齐工具
Table 3. Popular tools for short read alignment
工具 优点 下载链接 Bowtie2 支持间隙、局部和双端对齐模式 https://github.com/BenLangmead/bowtie2 BWA-MEM2 使用 FM 索引和8x压缩 https://github.com/bwa-mem2/bwa-mem2 Gapped BLAST 支持间隙对齐 https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi Subread 采用种子和投票策略 https://subread.sourceforge.net/ HISAT2 采用分层索引 https://github.com/DaehwanKimLab/hisat2 表 4 各类对齐后质量评估工具的评估指标
Table 4. Evaluation metrics for various post-alignment quality assessment tools
评估指标 Picard QPLOT Qualimap2 SAMstat verifyBamID 映射率 √ √ √ √ 插入尺寸 √ √ √ 序列重复水平 √ √ √ 碱基分布 √ √ √ √ 映射质量 √ √ √ √ 覆盖深度 √ √ √ GC含量 √ √ √ 错配率 √ √ √ √ 覆盖深度 √ √ 覆盖率 √ √ 污染估计 √ √ √ 表 5 各类对齐后质量评估工具的特点和下载链接
Table 5. Characteristics and download links for various post-alignment quality assessment tools
工具 特点 下载链接 SAMstat 评估指标统计 https://samstat.sourceforge.net/ QPLOT 评估指标统计 https://github.com/statgen/qplot Qualimap2 多样本处理 http://qualimap.conesalab.org/ Picard 自定义所需评估指标 https://github.com/broadinstitute/picard verifyBamID 检测污染 https://github.com/Griffan/VerifyBamID 表 6 流行的短读取对齐工具
Table 6. Popular tools for short read alignment
工具 方法 下载链接 VarScan2 启发式方法 https://github.com/dkoboldt/varscan SomaticSniper 联合基因型分析 https://github.com/genome/somatic-sniper SAMtools 联合基因型分析 https://github.com/samtools/samtools Strelka 等位基因频率分析 https://github.com/target/strelka MuTect 等位基因频率分析 https://github.com/broadinstitute/mutect MuTect2 单倍型模型 https://github.com/broadinstitute/gatk FreeBayes 单倍型模型 https://github.com/freebayes/freebayes Strelka2 分层单倍型模型 https://github.com/Illumina/strelka 表 7 各类变异可信度质量评估工具的特点和下载链接
Table 7. Characteristics and download links for various mutation confidence quality assessment tools
工具 特点 下载链接 hap.py 将 VCF 与标准数据集进行比较 https://github.com/Illumina/hap.py rtg-tools 在单倍型水平上进行变异比较 https://github.com/RealTimeGenomics/rtg-tools/ vgraph 使用变异图比较遗传变异 https://github.com/bioinformed/vgraph/ VBT-TrioAnalysis 变体比较和孟德尔违规检测 https://github.com/sbg/VBT-TrioAnalysis -
[1] Schloss J A. How to get genomes at one ten-thousandth the cost [J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2008, 26(10): 1113-1115. doi: 10.1038/nbt1008-1113 [2] Reuter J A, Spacek D V, Snyder M P. High-Throughput Sequencing Technologies [J]. Molecular Cell, 2015, 58(4): 586-597. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.05.004 [3] Hu T, Chitnis N, Monos D, et al. Next-generation sequencing technologies: An overview [J]. Hum Immunol, 2021, 82(11): 801-811. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2021.02.012 [4] Endrullat C, Glokler J, Franke P, et al. Standardization and quality management in next-generation sequencing [J]. Appl Transl Genom, 2016, 10: 2-9. [5] Chen S, Zhou Y, Chen Y, et al. fastp: an ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor [J]. Bioinformatics, 2018, 34(17): i884-i890. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty560 [6] Wang J, Raskin L, Samuels D C, et al. Genome measures used for quality control are dependent on gene function and ancestry [J]. Bioinformatics, 2015, 31(3): 318-323. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu668 [7] Paszkiewicz K H, Farbos A, O'neill P, et al. Quality control on the frontier [J]. Front Genet, 2014, 5: 157. [8] Sprang M, Kruger M, Andrade-Navarro M A, et al. Statistical guidelines for quality control of next-generation sequencing techniques [J]. Life Sci Alliance, 2021, 4(11): 65. [9] Bedre R, Avila C, Mandadi K. HTSQualC is a flexible and one-step quality control software for high-throughput sequencing data analysis [J]. Sci Rep, 2021, 11(1): 18725. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-98124-3 [10] Albrecht S, Sprang M, Andrade-Navarro M A, et al. seqQscorer: automated quality control of next-generation sequencing data using machine learning [J]. Genome Biol, 2021, 22(1): 75. doi: 10.1186/s13059-021-02294-2 [11] Institute B. FastQC: A quality control tool for high throughput sequence data [EB/OL]. 2023-05-17.https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/. [12] Wingett S W, Andrews S. FastQ Screen: A tool for multi-genome mapping and quality control [J]. F1000Res, 2018, 7: 1338. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.15931.1 [13] Okonechnikov K, Conesa A, Garcia-Alcalde F. Qualimap 2: advanced multi-sample quality control for high-throughput sequencing data [J]. Bioinformatics, 2016, 32(2): 292-294. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btv566 [14] He X, Chen S, Li R, et al. Comprehensive fundamental somatic variant calling and quality management strategies for human cancer genomes [J]. Brief Bioinform, 2021, 22(3): 1-15. [15] Cock P J, Fields C J, Goto N, et al. The Sanger FASTQ file format for sequences with quality scores, and the Solexa/Illumina FASTQ variants [J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2010, 38(6): 1767-1771. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp1137 [16] Ewing B, Green P. Base-Calling of Automated Sequencer Traces Using Phred. II. Error Probabilities [J]. 1998, 8(3): 186-194. [17] Iso. Genomics informatic — Quality control metrics for DNA sequencing: ISO/TC 215/SC 1 [S]. Genomics Informatics, 2020. [18] Yang X, Liu D, Liu F, et al. HTQC: a fast quality control toolkit for Illumina sequencing data [J]. BMC Bioinformatics, 2013, 14: 33. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-14-33 [19] Patel R K, Jain M. NGS QC Toolkit: a toolkit for quality control of next generation sequencing data [J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(2): e30619. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030619 [20] Cox M P, Peterson D A, Biggs P J. SolexaQA: At-a-glance quality assessment of Illumina second-generation sequencing data [J]. BMC Bioinformatics, 2010, 11: 485. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-485 [21] Chen Y, Chen Y, Shi C, et al. SOAPnuke: a MapReduce acceleration-supported software for integrated quality control and preprocessing of high-throughput sequencing data [J]. Gigascience, 2018, 7(1): 1-6. [22] Zhang T, Luo Y, Liu K, et al. BIGpre: a quality assessment package for next-generation sequencing data [J]. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics, 2011, 9(6): 238-244. doi: 10.1016/S1672-0229(11)60027-2 [23] Yin Z, Zhang H, Liu M, et al. RabbitQC: high-speed scalable quality control for sequencing data [J]. Bioinformatics, 2021, 37(4): 573-574. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btaa719 [24] Alser M, Rotman J, Deshpande D, et al. Technology dictates algorithms: recent developments in read alignment [J]. Genome Biol, 2021, 22(1): 249. doi: 10.1186/s13059-021-02443-7 [25] Canzar S, Salzberg S L. Short Read Mapping: An Algorithmic Tour [J]. Proc IEEE Inst Electr Electron Eng, 2017, 105(3): 436-458. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2015.2455551 [26] Liao Y, Smyth G K, Shi W. The Subread aligner: fast, accurate and scalable read mapping by seed-and-vote [J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2013, 41(10): e108. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt214 [27] Wilton R, Szalay A S. Performance optimization in DNA short-read alignment [J]. Bioinformatics, 2022, 41(10): e108. [28] Langmead B, Trapnell C, Pop M, et al. Ultrafast and memory-efficient alignment of short DNA sequences to the human genome [J]. Genome Biol, 2009, 38(8): 2081-2087. [29] Langmead B, Salzberg S L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2 [J]. Nat Methods, 2012, 9(4): 357-359. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1923 [30] Li H, Durbin R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform [J]. Bioinformatics, 2009, 25(14): 1754-1760. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp324 [31] Altschul S F, Gish W, Miller W, et al. Basic local alignment search tool [J]. J Mol Biol, 1990, 215(3): 403-410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2 [32] Altschul S F, Madden T L, Schaffer A A, et al. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs [J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 1997, 25(17): 3389-3402. doi: 10.1093/nar/25.17.3389 [33] Li H, Ruan J, Durbin R. Mapping short DNA sequencing reads and calling variants using mapping quality scores [J]. Genome Res, 2008, 18(11): 1851-1858. doi: 10.1101/gr.078212.108 [34] Kim D, Paggi J M, Park C, et al. Graph-based genome alignment and genotyping with HISAT2 and HISAT-genotype [J]. Nat Biotechnol, 2019, 37(8): 907-915. doi: 10.1038/s41587-019-0201-4 [35] Li H, Handsaker B, Wysoker A, et al. The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools [J]. Bioinformatics, 2009, 25(16): 2078-2079. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp352 [36] Iso. Biotechnology — Massively parallel sequencing —Part 2: Quality evaluation of sequencing data: ISO/TC 276[S]. Biotechnology, 2021. [37] Lassmann T, Hayashizaki Y, Daub C O. SAMStat: monitoring biases in next generation sequencing data [J]. Bioinformatics, 2011, 27(1): 130-131. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btq614 [38] Garcia-Alcalde F, Okonechnikov K, Carbonell J, et al. Qualimap: evaluating next-generation sequencing alignment data [J]. Bioinformatics, 2012, 28(20): 2678-2679. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts503 [39] Li B, Zhan X, Wing M K, et al. QPLOT: a quality assessment tool for next generation sequencing data [J]. Biomed Res Int, 2013, 2013: 865181. [40] Jun G, Flickinger M, Hetrick K N, et al. Detecting and estimating contamination of human DNA samples in sequencing and array-based genotype data [J]. Am J Hum Genet, 2012, 91(5): 839-848. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2012.09.004 [41] Xu C. A review of somatic single nucleotide variant calling algorithms for next-generation sequencing data [J]. Comput Struct Biotechnol J, 2018, 16: 15-24. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2018.01.003 [42] Koboldt D C, Zhang Q, Larson D E, et al. VarScan 2: somatic mutation and copy number alteration discovery in cancer by exome sequencing [J]. Genome Res, 2012, 22(3): 568-576. doi: 10.1101/gr.129684.111 [43] Li H. A statistical framework for SNP calling, mutation discovery, association mapping and population genetical parameter estimation from sequencing data [J]. Bioinformatics, 2011, 27(21): 2987-2993. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btr509 [44] Saunders C T, Wong W S, Swamy S, et al. Strelka: accurate somatic small-variant calling from sequenced tumor-normal sample pairs [J]. Bioinformatics, 2012, 28(14): 1811-1817. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts271 [45] Cibulskis K, Lawrence M S, Carter S L, et al. Sensitive detection of somatic point mutations in impure and heterogeneous cancer samples [J]. Nat Biotechnol, 2013, 31(3): 213-219. doi: 10.1038/nbt.2514 [46] Kim S, Scheffler K, Halpern A L, et al. Strelka2: fast and accurate calling of germline and somatic variants [J]. Nat Methods, 2018, 15(8): 591-594. doi: 10.1038/s41592-018-0051-x [47] Danecek P, Auton A, Abecasis G, et al. The variant call format and VCFtools [J]. Bioinformatics, 2011, 27(15): 2156-2158. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btr330 [48] Krusche P, Trigg L, Boutros P C, et al. Best practices for benchmarking germline small-variant calls in human genomes [J]. Nat Biotechnol, 2019, 37(5): 555-560. doi: 10.1038/s41587-019-0054-x [49] Cohort F T. 中华家系1号 [EB/OL]. 2023-05-17.https://chinese-quartet.org/. [50] Zhang F, Kang H M. FASTQuick: rapid and comprehensive quality assessment of raw sequence reads [J]. Gigascience, 2021, 10(2): 143768. [51] Darby C A, Gaddipati R, Schatz M C, et al. Vargas: heuristic-free alignment for assessing linear and graph read aligners [J]. Bioinformatics, 2020, 36(12): 3712-3718. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btaa265 [52] Wilton R, Budavari T, Langmead B, et al. Arioc: high-throughput read alignment with GPU-accelerated exploration of the seed-and-extend search space [J]. PeerJ, 2015, 3: e808. doi: 10.7717/peerj.808 [53] Piccolo S R, Frampton M B. Tools and techniques for computational reproducibility [J]. Gigascience, 2016, 5(1): 30. doi: 10.1186/s13742-016-0135-4 [54] Garijo D, Kinnings S, Xie L, et al. Quantifying reproducibility in computational biology: the case of the tuberculosis drugome [J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(11): e80278. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080278 [55] Loman N, Watson M. So you want to be a computational biologist? [J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2013, 31(11): 996-998. doi: 10.1038/nbt.2740 [56] Bray N L, Pimentel H, Melsted P, et al. Near-optimal probabilistic RNA-seq quantification [J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2016, 34(5): 525-527. doi: 10.1038/nbt.3519 [57] Steinbiss S, Silva-Franco F, Brunk B, et al. Companion: a web server for annotation and analysis of parasite genomes [J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2016, 44(W1): W29-W34. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw292 [58] Jun G, Wing M K, Abecasis G R, et al. An efficient and scalable analysis framework for variant extraction and refinement from population-scale DNA sequence data [J]. Genome Res, 2015, 25(6): 918-925. doi: 10.1101/gr.176552.114 [59] Di Tommaso P, Chatzou M, Floden E W, et al. Nextflow enables reproducible computational workflows [J]. Nat Biotechnol, 2017, 35(4): 316-319. doi: 10.1038/nbt.3820 [60] Vivian J, Rao A A, Nothaft F A, et al. Toil enables reproducible, open source, big biomedical data analyses [J]. Nat Biotechnol, 2017, 35(4): 314-316. doi: 10.1038/nbt.3772 [61] Molder F, Jablonski K P, Letcher B, et al. Sustainable data analysis with Snakemake [J]. F1000Res, 2021, 10: 33. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.29032.2 [62] Galaxy C. The Galaxy platform for accessible, reproducible and collaborative biomedical analyses: 2022 update [J]. Nucleic Acids Res , 2016(W1): W3-W10. [63] Oliver H, Shin M, Matthews D, et al. Workflow Automation for Cycling Systems [J]. Computing in Science & Engineering, 2019, 21(4): 7-21. [64] Li J, Jew B, Zhan L, et al. ForestQC: Quality control on genetic variants from next-generation sequencing data using random forest [J]. PLoS Comput Biol, 2019, 15(12): e1007556. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1007556 -


 作者投稿
作者投稿 专家审稿
专家审稿 编辑办公
编辑办公


 下载:
下载: