Comparison of Direct Comparison Method in VNA and Power Transfer Standard Measurements
-
摘要: 校准因子是用于表征射频功率传感器示数准确度的参数,定义为功率传感器显示功率和入射功率的比值,它是功率量值传递的对象。介绍了直接比较法和基于VNA的直接比较法的组成与测量原理,阐述了等效源反射系数在直接比较法里的应用,并使用直接比较法和基于VNA的直接比较法测量了 Rohde Schwarz NRP50T 功率传感器的校准因子。测量结果显示,两种方法测量的修正后校准因子之间的最大差异为3.056%,基于VNA的直接比较法的等效源反射系数一般大于直接比较法,直接比较法不确定度评定方法成熟,仍是目前最主流的射频功率传感器校准方法。Abstract: The calibration factor is a parameter used to characterize the reading accuracy of RF power sensors, defined as the ratio of the power displayed by the sensor to the incident power. It is the object of power value transfer. This paper introduces the composition and measurement principles of the direct comparison method and the VNA-based direct comparison method. It describes the application of the equivalent source reflection coefficient in the direct calibration method. The calibration factor of the Rohde & Schwarz NRP50T power sensor was measured using both the direct calibration method and the VNA-based direct comparison method. Results show that the maximum difference between the corrected calibration factors measured by the two methods is 3.056%. The equivalent source reflection coefficient of the VNA-based direct comparison method is generally larger than that of the direct comparison method. The uncertainty evaluation method for the direct comparison method is well-established, making it currently the most prevalent RF power sensor calibration method.
-
0. 引言
无线电技术对于移动通信、航空航天、雷达导航、气象遥感、临床医学等领域有着广泛而深远的影响,涉及国民经济和人民生活的方方面面。功率参数是无线电技术的基本参数之一,在无线电技术应用中具有重要作用[1 - 2]。
射频和微波功率传感器与功率指示器组成功率计,功率计是通信、广播、电视、雷达、宇航等技术领域不可缺少的功率测量仪器。功率传感器由接头、功率敏感部件、直流或低频电路等部分组成,功率传感器有多种类型,按工作原理可以分为热敏电阻型功率传感器、热偶型功率传感器和二极管型功率传感器等,按接头的型式可以分为同轴型功率传感器和波导型功率传感器[3 - 4]。
校准因子是用于表征射频功率传感器示数准确度的参数,其定义为功率传感器显示的功率和入射功率的比值。它是功率量值传递的对象,对功率传感器校准的方法有交替比较法、传递标准法与直接比较法 [5 − 8]。
交替比较法特指标准功率计与被测功率计直接在信号源输出端面进行交替比较的方法,通常仅限于对测量不确定度要求较低的场合(5%),一般工作频率在18GHz 以下。
传递标准法用标准功率计定标传递标准并将传递标准作为单独设备使用,缺点是由于构成传递标准的器件被“永久性”地连接在了一起,长时间使用后其相关散射参数难以被测得。
直接比较法是将标准功率计与被测功率计在等效信号源的测量端面进行比较,并使用等效源反射系数[9 − 12]进行失配误差修正和不确定度评定,是目前最主流的校准方法。
直接比较法进行校准时,需要信号源与功率分配器或定向耦合器构成等效信号源降低失配影响,还需用到标准射频功率传感器,监测射频传感器、功率计以及射频和直流连接电缆等。直接比较法可以通过测量标准射频传感器与待测射频传感器的反射系数,与等效源反射系数一起对测量结果进行误差修正[13 − 16]。
直接比较法校准射频功率传感器所需的设备在矢量网络分析仪(VNA)中都是存在的,文献[17]提出了用VNA来实现功率校准,可以使用VNA内部的信号源,定向耦合器和接收机进行功率传感器的校准,增加了便利性,对专用的设备要求较小,一般的射频实验室可能没有专用的功率传递标准,或者因其他仪器受限而无法进行功率传感器校准,基于VNA的方法可以成为备选的方法。
早期VNA的功率水平与频段范围受限,其内部信号源易受其他信号的干扰,用来做功率传感器的校准有一定的局限性。现代矢量网络分析仪性能的提高使得利用矢量网络分析仪进行功率传感器校准成为可能 [18 − 24]。
本文介绍了传统的直接校准法和基于VNA的直接比较法的组成与测量原理,阐述了失配修正项等效源反射系数在直接比较法中的应用,在0~50GHz频率范围内和传统的直接比较法进行了对比实验,比较了两种进行失配修正的误差项,并对实验获得的校准因子数据结果进行了分析。
1. 直接比较法原理
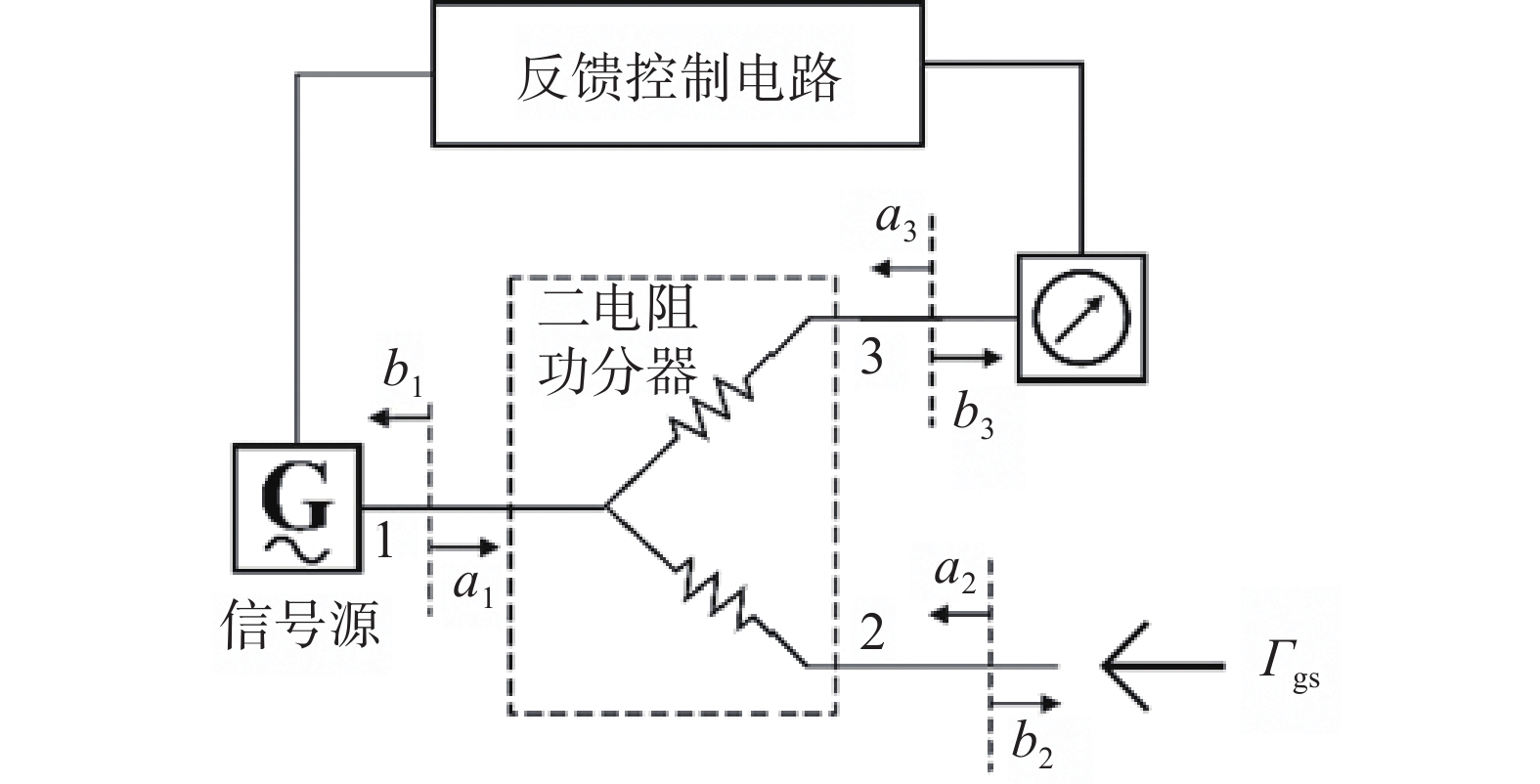
如图1所示,直接比较法测量系统由射频信号发生器、功率分配器(或定向耦合器)和连接到功率分配器输出端口之一的参考功率传感器组成。
在信号源之后连接功率分配器,以便于信号源的输出与监测功率传感器示数成比例显示,标准功率传感器和待测功率传感器交替连接到测量端口。
直接比较法测量原理是先用标准功率计确定传递标准的校准因子Ks,相当于得到了一个标准信号源,然后再用已知校准因子的信号源去校准被测功率计。
直接比较法的校准因子计算公式为:
Ku=KsPcsPcuPbuPbsM (1) 式中,Ku为待测功率传感器的校准因子;Ks为标准功率传感器的校准因子;Pbu为待测功率传感器的功率;Pbs为标准功率传感器的功率;Pcu为当待测功率传感器连接到测量系统时监测功率计的功率;Pcs为当标准功率传感器连接到测量系统时监测功率计的功率。
式(1)中,M为失配因子,失配是影响高频和微波功率测量结果不确定度的最主要因素,减小并准确评估失配影响成为降低测量不确定度的必然要求。
失配程度与等效信号源反射系数和负载反射系数有关,实际校准工作中,常把失配因子定为1,如果没有采取有效措施,由失配误差引入的不确定度在微波频段就可能达到5%,在毫米波段可能会达到10%甚至更高,因此有必要对失配项进行准确评估。
M=MuMs=|1−ΓgeΓu|2|1−ΓgeΓs|2 (2) 式中,Mu和Ms分别为连接被测功率传感器和标准传感器时的失配因子;Гu为待测功率传感器的反射系数;Гs为标准功率传感器的反射系数;Гge为标准功率传感器和待测功率传感器连接到的功率分配器等效源反射系数。以上反射系数均为复数量,在直接比较法中需要额外进行S参数测量。
2. 等效源反射系数
信号源和三端口取样器件在闭环状态下构成稳幅信号源,如图2所示。
图2为稳幅信号源测量装置示意图,将稳幅信号源的电压反射系数记作Гg,表示为:
Γg=S22−S21S32S31 (3) 直接比较法在开环状态下,利用三端口器件两电阻功分器或定向耦合器进行功率比值测量达到降低失配的目的[23]。
式(2)中,Mu和Ms分别为连接被测功率传感器和标准传感器时的失配因子,它们表示为:
Mu=|1−(S22−S21S32S31)Γu|2gMs=|1−(S22−S21S32S31)Γs|2 (4) 式(4)中,(S22−S21S32S31)项并不是测量端口的源电压反射系数,该项与图2所示的稳幅信号源的电压反射系数Гg的散射参数形式完全相同,因此被称作等效源反射系数,表示为:
Γge=S22−S21S32S31 (5) 等效源反射系数Гge仅取决于功率分配器或定向耦合器本身的散射参数,一般情况下它比信号源的源匹配的值要小,并且可以通过矢量网络分析仪进行测量。
测试该项的方法也有很多,例如散射参数法和Jureshek法、K.Shimaoka法[25 - 26],操作与计算比较复杂。VNA中信号发生器的源匹配可以由校准件校准完成后给出。
由于等效源反射系数的存在,直接比较法除了需要对待测功率传感器与标准功率传感器的功率比值进行测量外,还需要对所用三端口器件进行等效源反射系数测量。
3. 基于VNA的直接比较法原理
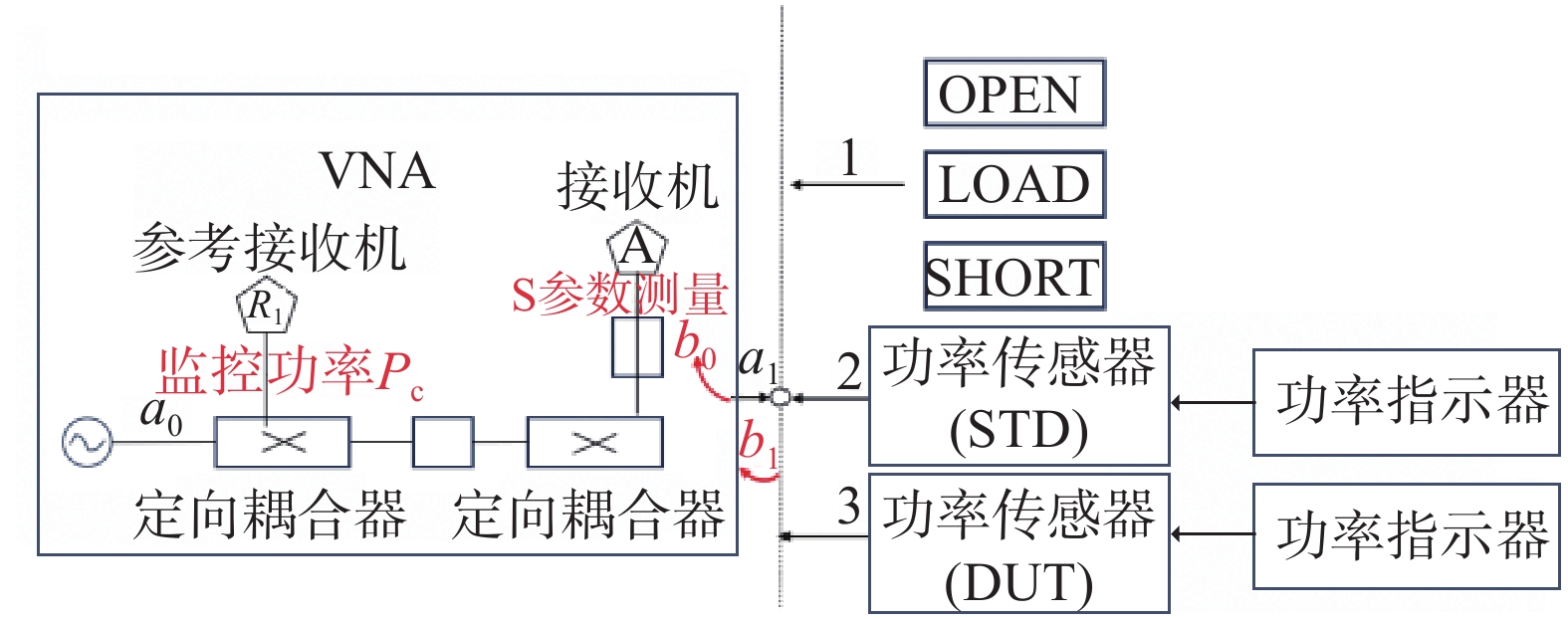
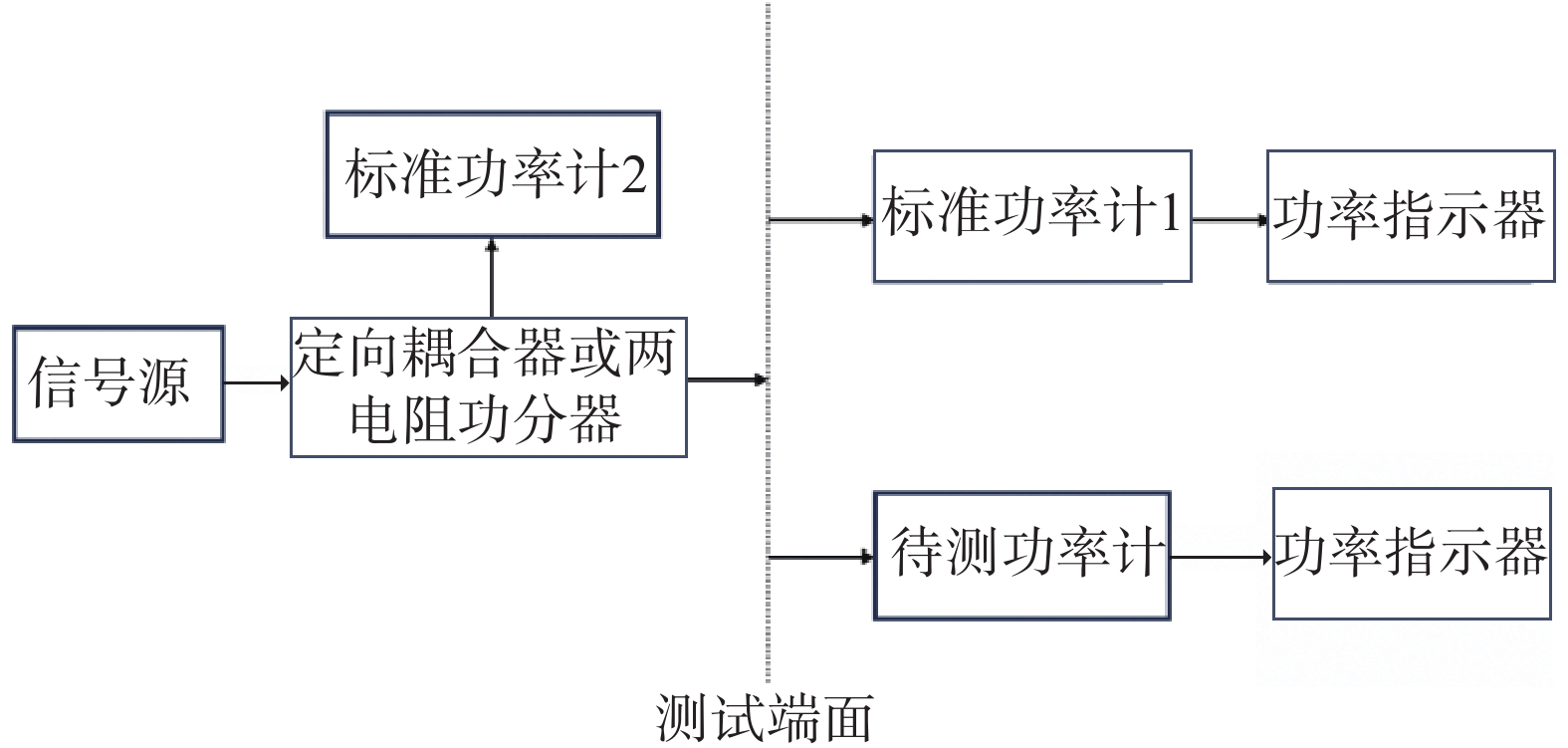
使用 VNA可以实现功率传感器的校准因子测量。如图3所示,VNA包含定向耦合器、接收机、信号发生器等,VNA 满足测量校准因子所需的所有组件[27 − 29]。
将图3与图1进行比较,图3中与定向耦合器耦合端口相连的R1接收器和图1中与功率分配器相连的监测功率传感器均可进行旁臂功率的监测。功率传感器校准因子的测量过程可通过一次网分校准,两次功率传感器的连接来完成。
首先对VNA进行单端口校准,校准完成后的端口依次连接标准功率传感器与待测功率传感器,在连接标准功率传感器或待测功率传感器时,参考接受机负责监测旁臂输出功率Pcu与Pcs,功率传感器的反射系数VNA与内部定向耦合器等效源反射系数均由VNA测量,标准功率传感器与待测功率传感器的功率示数由功率计显示读取。
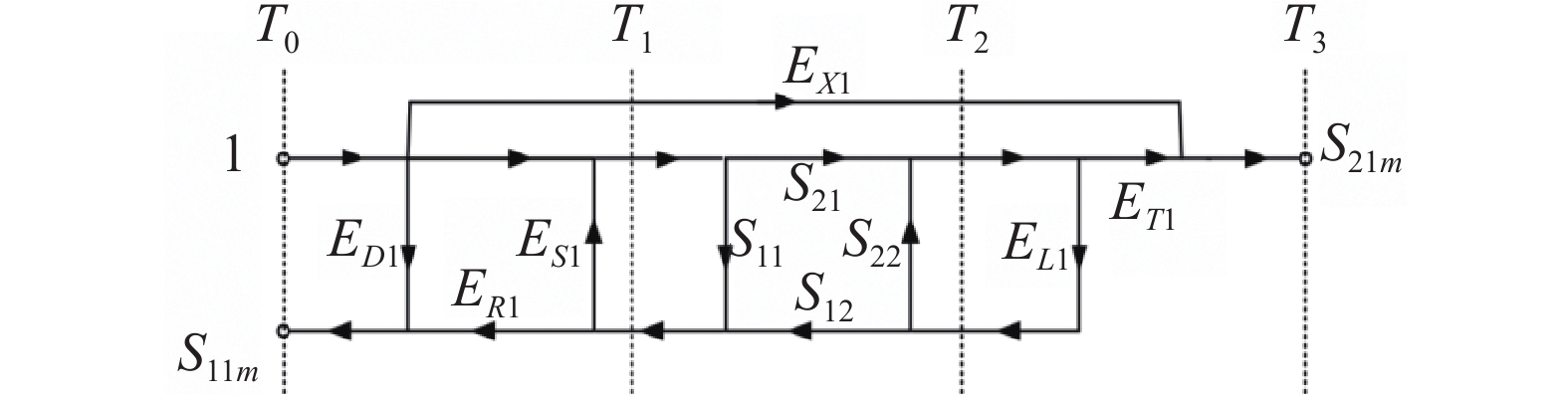
图4为VNA单端口误差模型图,VNA的误差项有方向性误差ED、源失配误差ES、反射跟踪误差ER、负载失配误差EL、传输跟踪误差ET、串扰误差EX,使用机械校准套件(OPEN,SHORT,LOAD)进行单端口校准,校准后VNA可以得到上述六项误差[30 − 31]。
在上述六项误差模型中,VNA端口的源阻抗失配误差ES1就是进行误差修正所需的等效源反射系数Гge。计算时,式(2)中用VNA端口的源阻抗失配误差ES项代替等效源反射系数Гge进行计算,查询VNA的编程手册可以找到对应的误差项读取指令,以上数据获得与计算均由计算机程序通过GPIB控制仪器执行。
4. 测量结果
为了对直接比较法与基于VNA的直接比较法进行对比,使用相同的标准射频功率传感器对同一待测射频功率传感器对进行校准。
使用了以下仪器装置进行了直接比较法的测量: Keysight 8257D 信号发生器、Rohde Schwarz NRX功率计、Rohde Schwarz NRPZ57 功率传感器作为旁臂监测功率计,两个Rohde Schwarz NRP50T 功率传感器分别作为标准功率传感器与待测功率传感器,HP1166C(DC~50 GHz) 电阻式功率分配器。首先测量了功率分配器的等效源反射系数,然后再进行比值测量。
使用了Keysight N5225B VNA、Rohde Schwarz NRX 功率计、两个Rohde Schwarz NRP50T 功率传感器、85056D 机械校准套件进行了基于VNA的直接比较法的测量。
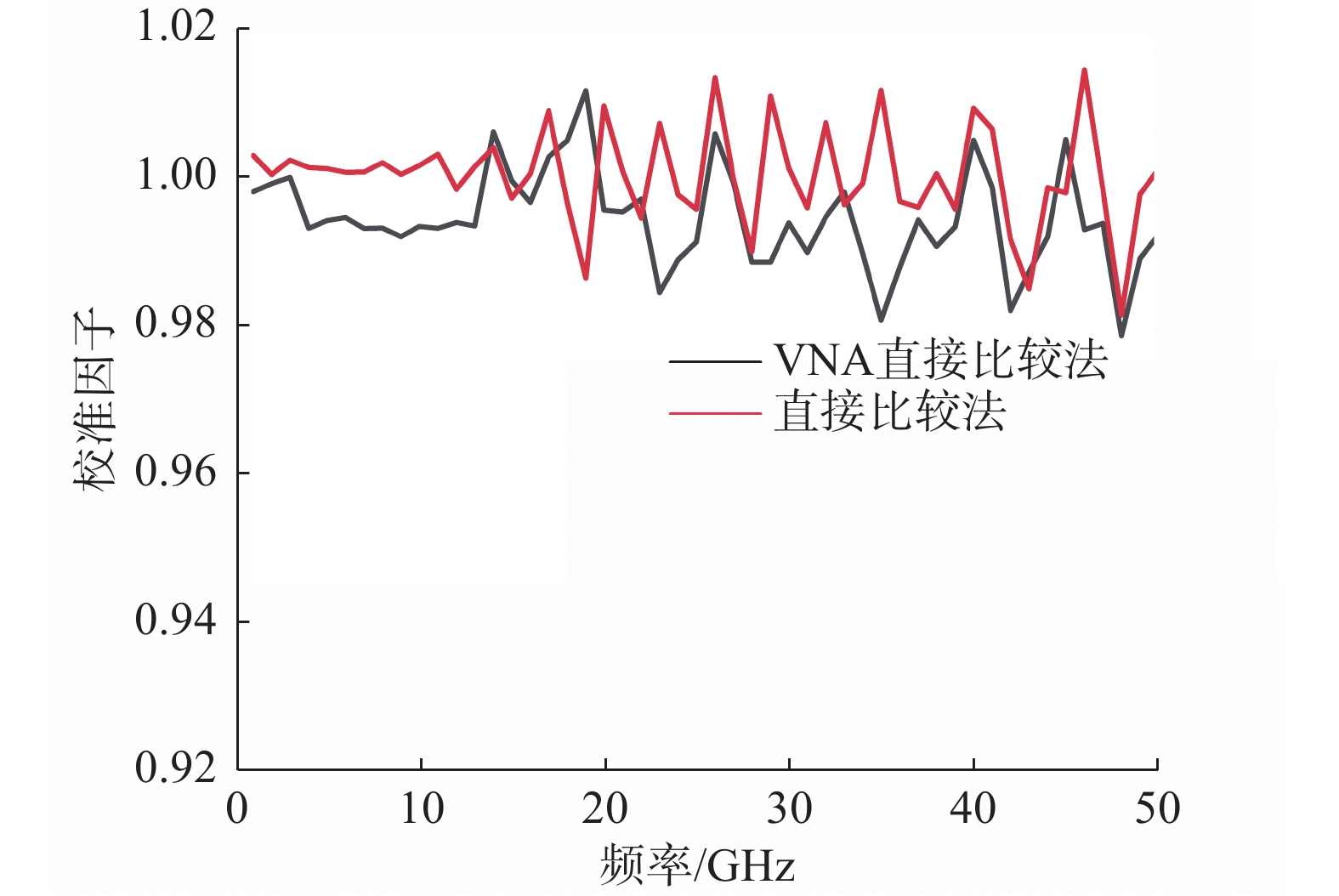
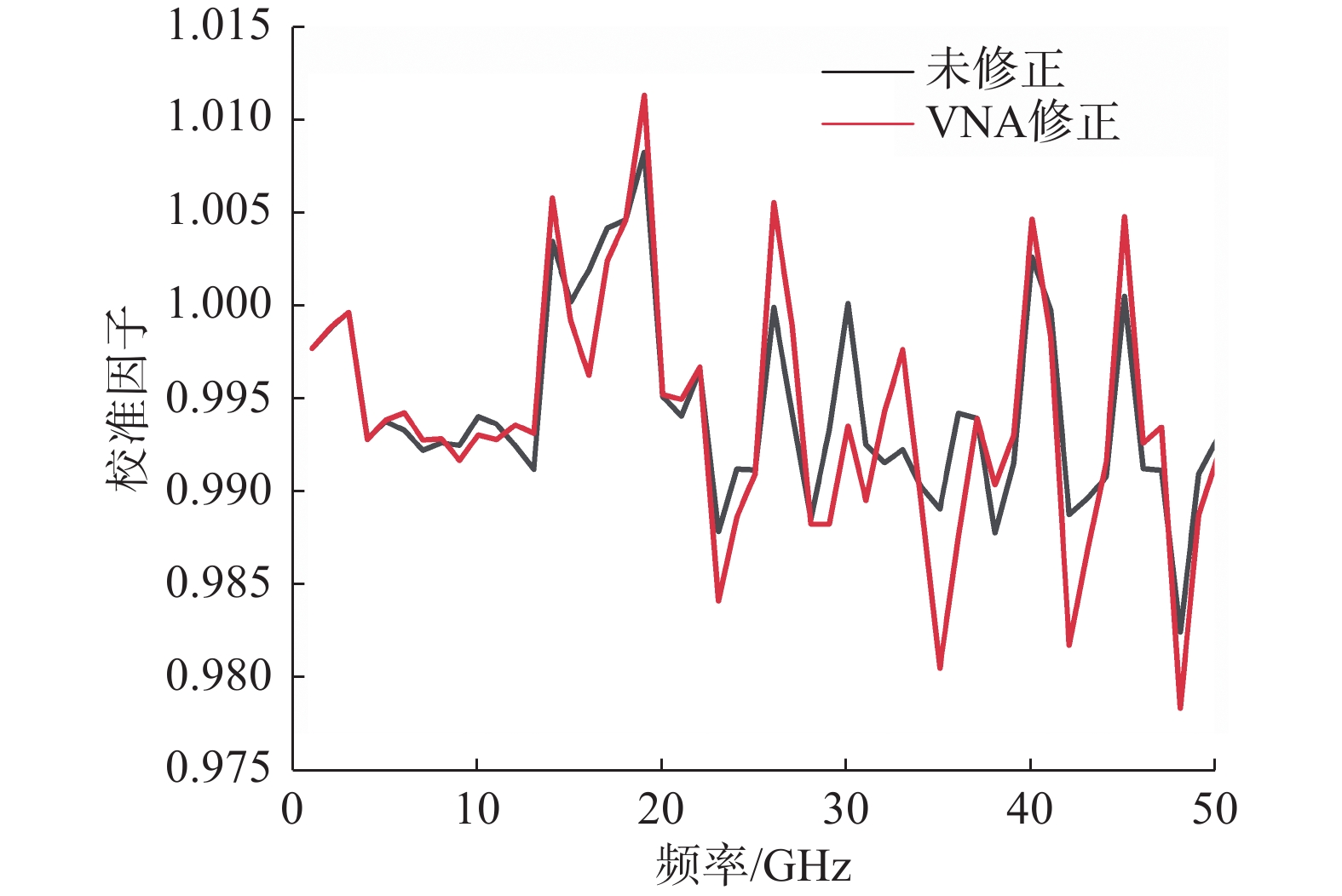
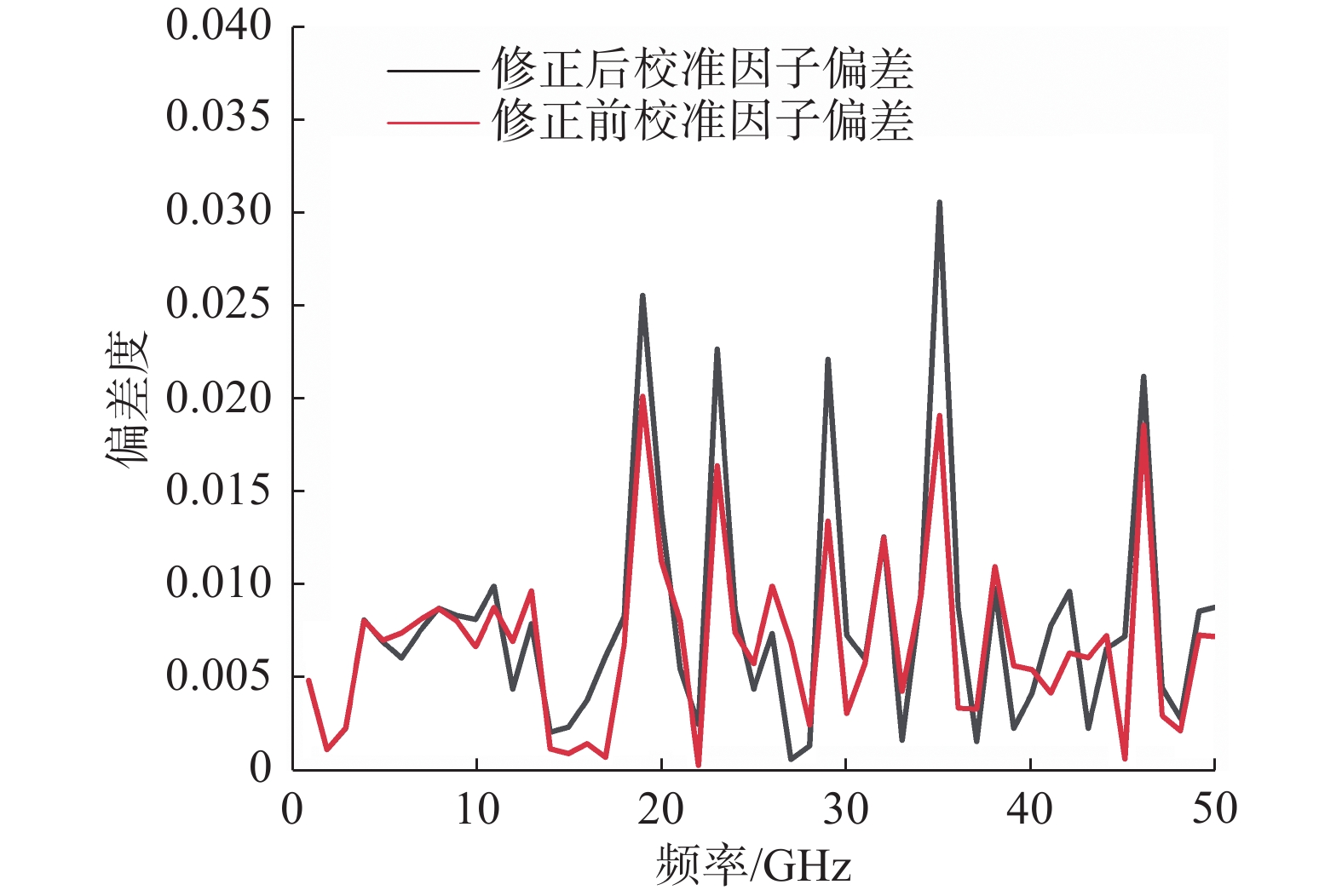
通过这两种不同方法获得的修正前后校准因子值如图5、图6所示,两种方法测量得到的矢量修正后的校准因子之间的最大差异为3.056%。
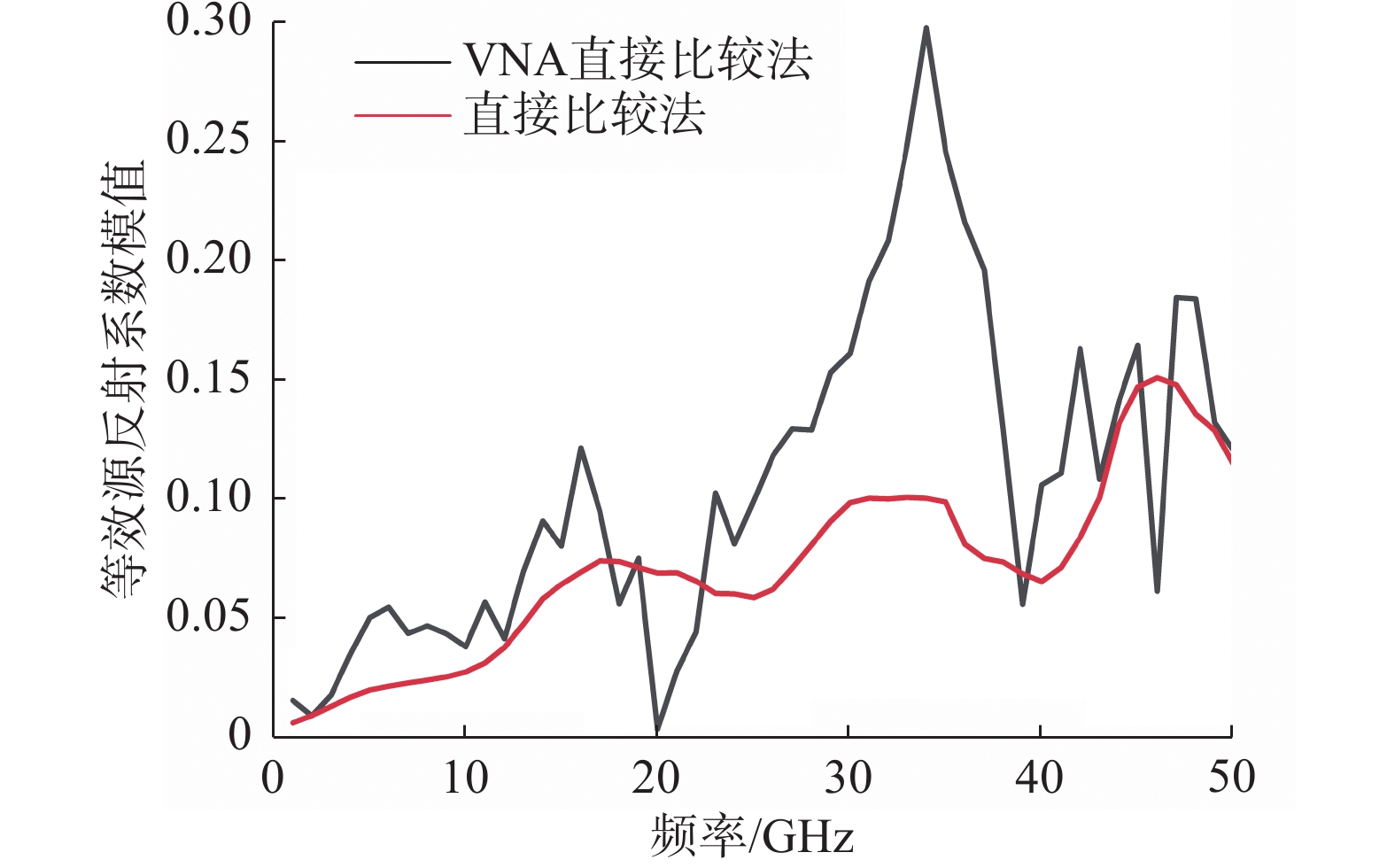
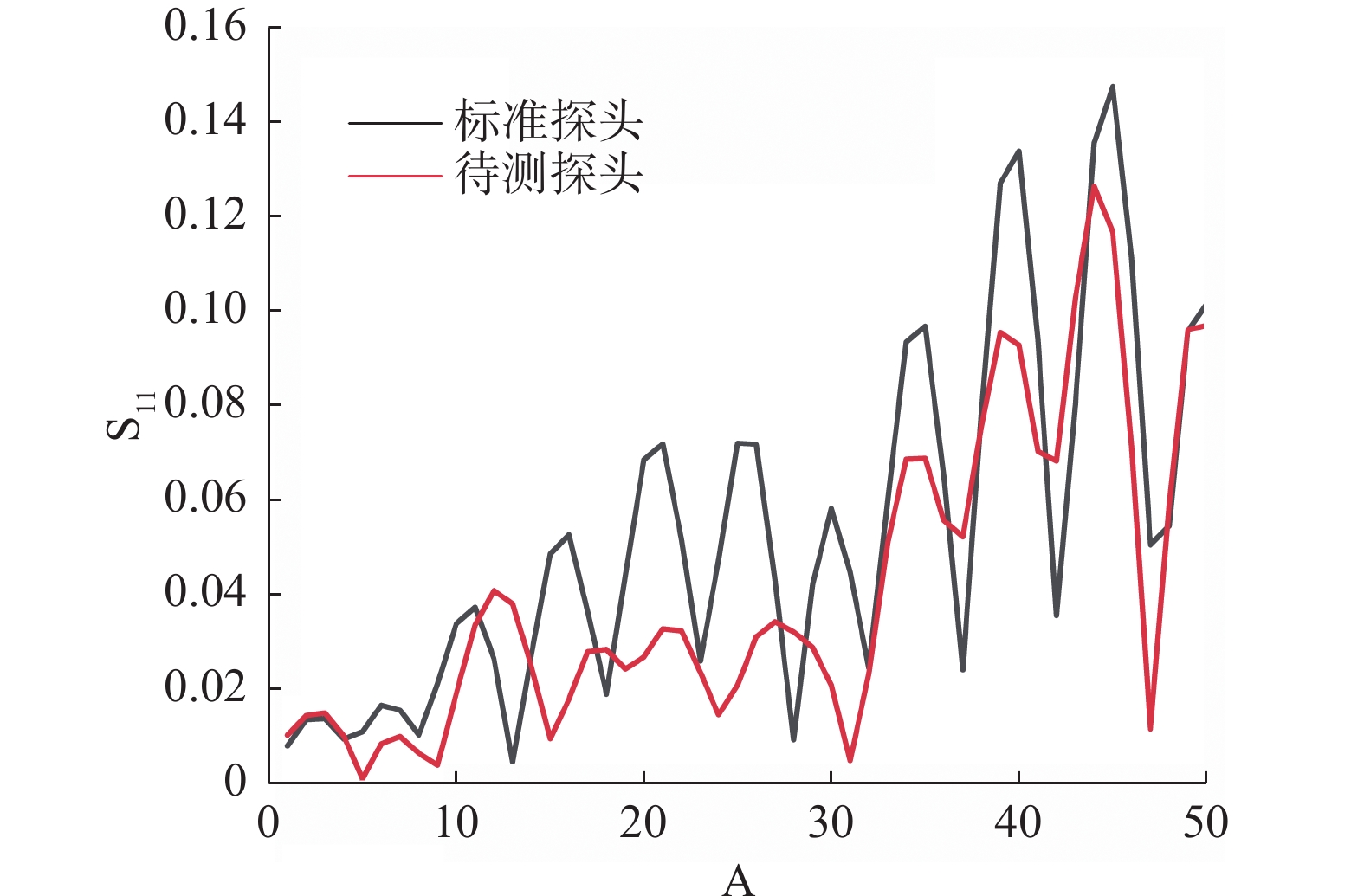
式(2)中用VNA端口的源阻抗失配误差项ES作为等效源反射系数Гge进行失配修正,图7对比了这两种方法在0~50GHz频率范围内的等效源反射系数模值大小。图8为待测与标准功率传感器的反射系数。
直接比较法的等效源反射系数由Keysight N5225B VNA测量功分器的各项S参数计算得到,VNA直接比较法的源匹配误差项ES由指令读取校准完成的Keysight N5225B VNA的误差项数据得到。
从图7可以看出,在整个目标频率范围内,功分器的等效源反射系数一般小于VNA校准完成后的源匹配。
如图9所示,VNA进行矢量修正前后的校准因子曲线变化还是比较大的,因为图7中测得的源匹配误差项在35 GHz处达到了0.3。
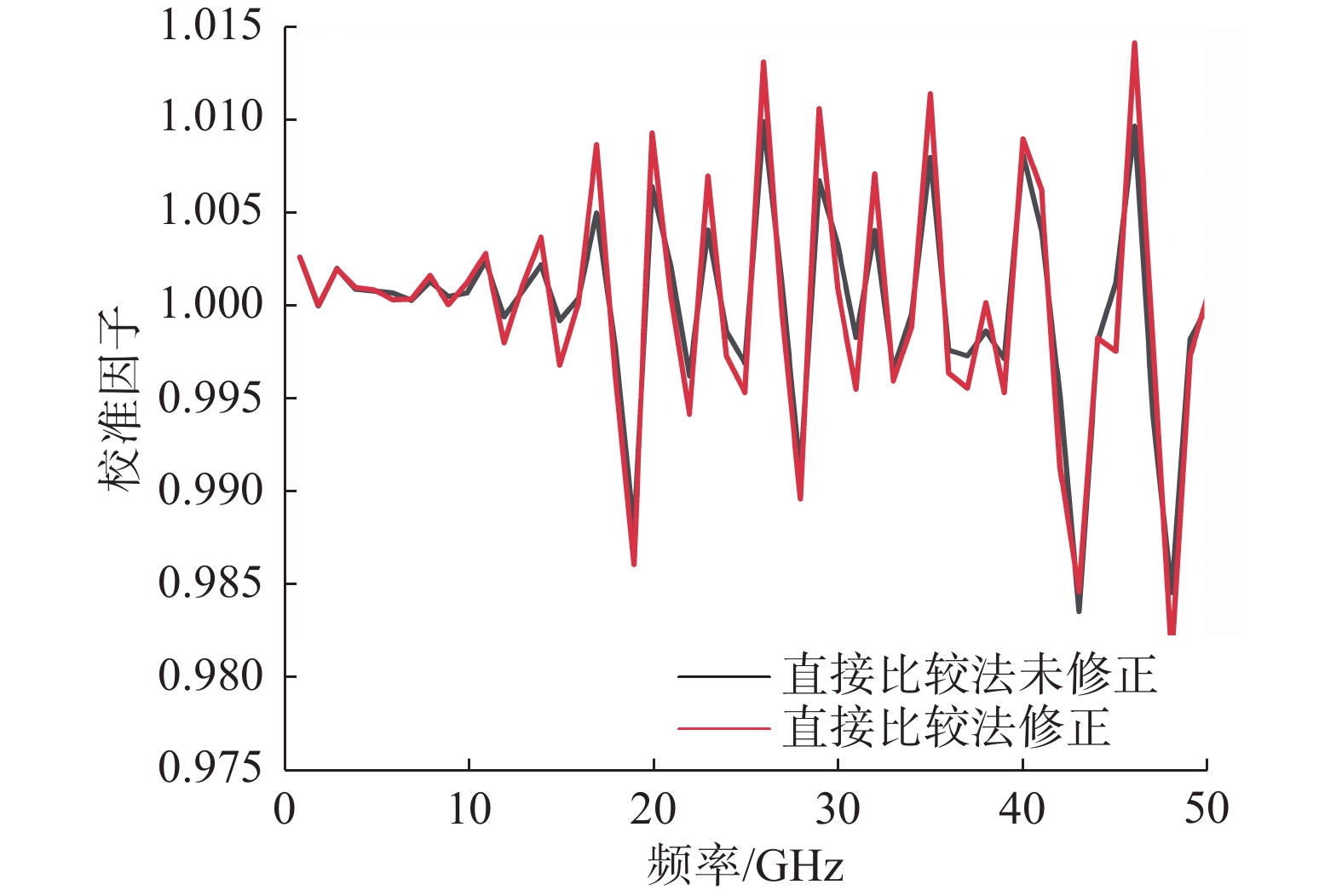
如图10所示,直接比较法由于进行误差修正的等效源反射系数较小,修正前后的校准因子变化相比基于VNA的直接比较法小。
如图11所示,经过矢量修正后的校准因子偏差有所降低。基于VNA的直接比较法能够直接由指令读取到VNA的误差项数据,自动进行宽频带的矢量修正,相比于直接比较法避免了复杂的等效源反射系数的测量,操作更加简便,数据处理更加方便。
基于VNA的直接比较法也有自身的局限性,例如内部信号源与接收机的功率电平的稳定性不如直接比较法的信号源功率电平稳定,进行矢量修正的等效源反射系数不仅决于使用的VNA自身内部的三端口器件的优劣,还与测量端口的校准结果有关,受到的影响较多。
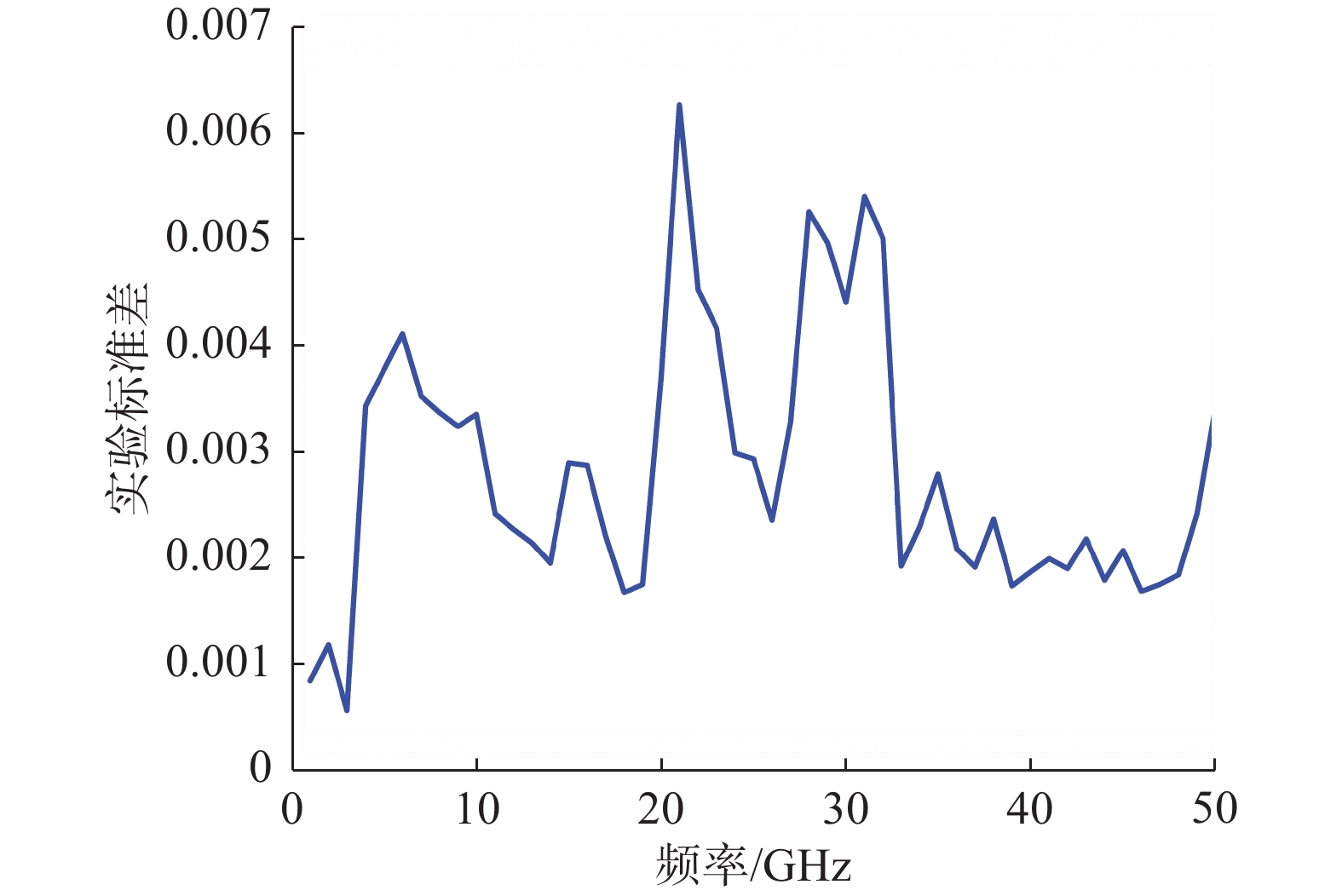
此外,在0 dbm的功率电平下对基于VNA的直接比较法进行了6次重复性实验,从图12可以看到在全频段内标准差大部分在0.006以下,重复性在可接受的范围内。
5. 结论
功率参数是无线电最基本、最重要的参数之一,也是无线电计量体系中其它多个参数的源头,校准因子是用于表征射频功率传感器示数准确性的参数,它是功率量值传递的对象,功率传感器的校准的方法有交替比较法,直接比较法与传递标准法。
本文介绍了直接比较法和基于VNA的直接比较法的测量原理与装置组成,分别使用直接比较法和基于VNA的直接比较法测量了 Rohde Schwarz NRP50T 功率传感器的校准因子,并对这两种校准方法的等效源反射系数进行了比较。基于VNA的直接校准法获得的等效源反射系数一般大于直接比较法,两种方法测量的校准因子之间的最大差异为3.056%,直接比较法不确定度评定方法成熟,仍是目前最主流的射频功率传感器校准方法。
-
[1] 冯新善. 高频、微波功率的计量测试[M]. 北京: 中国计量出版社, 1987: 123-136. [2] 孙伟杰. WR-15(50GHz-75GHz)微波功率国家基准测量技术研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2014. [3] 汤世贤. 微波测量[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 1991: 163-166. [4] 刘国林, 殷贯西. 电子测量[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2003: 112-133. [5] 孙新莉, 陈钢. RF/微波功率传感器校准方法的探讨[J]. 计量技术, 2007(6): 42-44. [6] 李勇, 崔孝海, 赵巍. 射频与微波功率传感器校准规范: JJF 1887-2020[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2020. [7] Shan Y, Cui X. RF and microwave power sensor calibration by direct comparison transfer[J]. Modern metrology concerns, 2012, 1: 175-200.
[8] R. A. Johnson. Understanding microwave power splitter[M]. Microwave Journal, 1975.
[9] 黎明, 李再奎, 史清林. 定向耦合器与检波器组成等效信号源反射系数的分析[J]. 齐齐哈尔师范学院学报(自然科学版), 1995, 15(2): 15-17. [10] 王晋淦. 信号发生器源反射系数的测量方法[J]. 电子测量与仪器学报, 1987, 1(3): 1-10. [11] 朱军, 李建一, 王增浩. 低反射系数等效信号源的测试方法研究[J]. 中国测试技术, 2008, 34(3): 34-36. [12] 张翠翠, 王益, 王建忠. 有源器件反射系数测量方法分析[J]. 太赫兹科学与电子信息学报, 2015, 13(2): 26-271. [13] 代明珍, 崔孝海, 刘欣萌. WR-28功率基准系统中等效源反射系数测量方法[J]. 计量学报, 2012, 33(1): 68-72. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1158.2012.01.15 [14] Kwon J Y, Kang T W, Kang J S, et al. A W-band millimeter-wave power standard transfer system using the direct comparison method[J]. The Journal of Korean Institute of Electromagnetic Engineering and Science, 2013, 24(1): 47-54. DOI: 10.5515/KJKIEES.2013.24.1.47
[15] Weidman M P. Direct comparison transfer of microwave power sensor calibrations[EB/OL]. https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/GOVPUB-C13-c6a1068e6a40dd8e571b21514d889d81/pdf/GOVPUB-C13-c6a1068e6a40dd8e571b21514d889d81.pdf.
[16] YUAN W, DING S, CUI X, et al. NIM Microwave Power Calibration and Measurement Capabilities[C]. 2020 13th UK-Europe-China Workshop on Millimetre-Waves and Terahertz Technologies (UCMMT), 2020.
[17] Aldossary F, Huneiti Z, Hunaiti Z, et al. The network analyser (HP8510C) as a transfer instrument for power sensor calibration[C]. 2008 IEEE Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference, 2008.
[18] Kızılbey O, Arslan M, Bayrak Y, et al. A Novel Software for Automatic Calibration Factor Measurement of RF Power Sensors[C]. 2022 7th International Conference on Computer Science and Engineering (UBMK), 2022.
[19] Szatkowski J. Developing RF Power Sensor Calibration Station in Direct Comparison Transfer System using Vector Network Analyzer[J]. Journal of Telecommunications and Information Technology, 2021(3): 18-22.
[20] Perangin-Angin W K. Development of RF Power Sensor Measurement System Using VNA Method and Heating Block[J]. MAPAN, 2023, 38(4): 805-813. DOI: 10.1007/s12647-023-00644-y
[21] Fantom A. Radio frequency & microwave power measurement[M]. IET, 1990.
[22] W. K. P. Angin, J. Kwon, T. Kang, et al. Comparison of RF power sensor calibration using a vector network analyzer and a direct transfer system[C]. URSI Asia Pacific Radio Science Conference, 2016.
[23] 张东云, 宋政辉, 潘晓, 等. 微波功率传感器自动校准系统设计与实现[J]. 计量科学与技术, 2022, 66(12): 46-49,54. DOI: 10.12338/j.issn.2096-9015.2021.0248 [24] Juroshek J R. A direct calibration method for measuring equivalent source mismatch[J]. Microwave Journal, 1997, 40(10): 106-113.
[25] CUI X, LI Y, GAO X, et al. Measurement and evaluation of the WR-28 calorimeter[C]. 77th ARFTG Microwave Measurement Conference, 2011.
[26] SHIMAOKA K, KINOSHITA M, INOUE T. A Broadband Waveguide Calorimeter in the Frequency Range From 50 to 110 GHz[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2013, 62(6): 1828-1833. DOI: 10.1109/TIM.2012.2225956
[27] HUANG Y, YUAN W, CUI X, et al. WR-42 Waveguide Microcalorimeter for Thermistor Mount Calibration[C]. 2018 Conference on Precision Electromagnetic Measurements (CPEM 2018), 2018.
[28] 刘欣萌. 高频和微波功率基准及其应用研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2007. [29] Jakubowski J. A study on the calibration of an HPM meter based on a D-dot sensor and logarithmic RF power detector[J]. Metrology and Measurement Systems, 2020, 1: 673-685.
[30] GU DZ, LU XF, LAMROZ B, et al. A self-calibrated transfer standard for microwave calorimetry[C]. Conference on Precision Electromagnetic Measurements, 2018.
[31] Wong K. Complete power sensor calibration using a VNA[C]. 80th ARFTG Microwave Measurement Conference, 2012.

 作者投稿
作者投稿 专家审稿
专家审稿 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: